Risk Management
Risk Management Policy
In response to changes in the Company's development strategy, TCC approved the amendment to its Risk Management Policy at the Board meeting on May 14, 2024, incorporating biodiversity as a key area of risk identification to prevent and mitigate the impact of operations on nature and biodiversity.
Organization Structure
The Risk Management Committee was established directly under the Board of Directors in May 2020. In 2021, the committee was re-elected, with the addition of a member with a legal background. It currently consists of three members, all independent directors with expertise in risk management, two of whom are women.

Risk Management Process
TCC refers to the World Economic Forum's (WEF) 2023-2024 Global Risk Report, cement and energy industry risk reports, and international trends to identify risks across seven dimensions, including product and service development. Based on the risk identification results, each department develops corresponding response strategies.
The Risk Management Committee reports to the Board of Directors on risk control at least once a year.
Operational Status
- Two meetings were held in 2021 (on August 10 and November 8), with 100% committee member attendance.
Reported on the annual updates to TCC's risk identification matrix, results of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) project, and content related to the ISO 37001 Anti-Bribery Management System implementation. - The third meeting of the second term was convened in 2022 (on August 5)
Reported on updates to TCC's risk identification matrix, outlined the impacts on operations and mitigation strategies in response to war, geopolitical issues, the energy transition, and demographic shifts. - The fourth and fifth meetings of the second term were convened in 2023 (on March 24 and November 10)
Reported on updates to TCC 's risk identification matrix, climate-related performance indicators and targets, and the potential impact of Taiwan's carbon fee collection in 2024 and payment in 2025. - Each year, TCC requires all employees to read the Risk Management Policy and complete a related assessment. With an estimated reading and assessment time of three minutes per person, a total of 15,684 employees participated in risk management education and training in 2023, accumulating 784.2 hours in total.
TCC's 2024 Risk Matrix
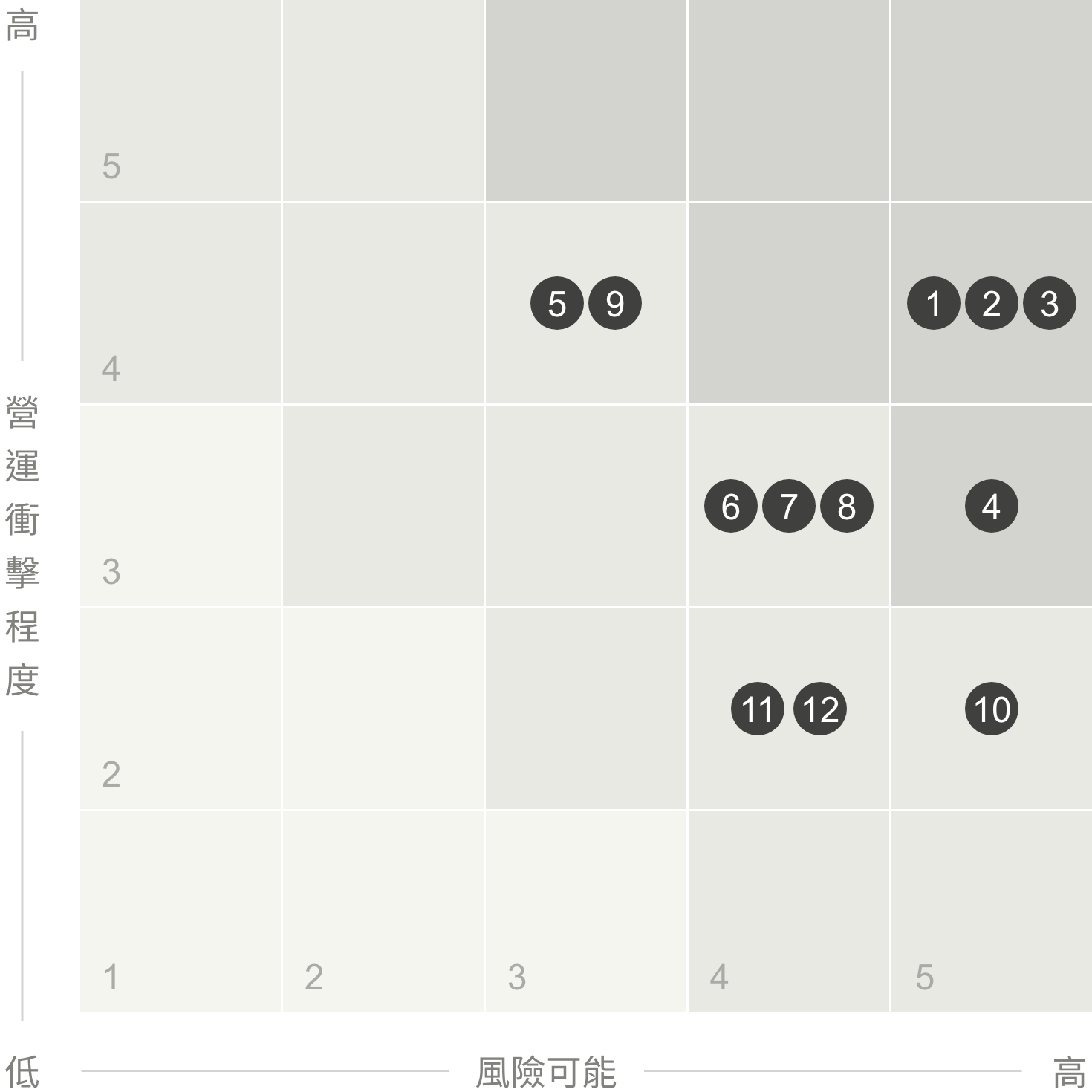
Cement Industry Development Risk in Mainland China
Exchange Rate, Interest Rate, and Financing Risks
Carbon Fees / Carbon Taxes / Carbon Trading
Natural Disasters - Earthquakes
Internationalization Strategy
Information Technology Security Risks
War and Geopolitical Conflicts
Compliance and Litigation Risks
Talent Recruitment and Succession (Including Salary and Incentives)
Climate Change - Natural Disasters (Typhoons, Floods, Droughts, Wildfires)
Rising Prices for Raw Materials (Fuel) and Substitutes
Biodiversity
| Risks Faced by TCC | Risk Factor Description | Mitigation Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Cement Industry Development Risks in Mainland China | Due to real estate regulation in Mainland China and the gradual saturation of infrastructure development, cement demand has declined. |
|
| Carbon fees/ Carbon Trading |
| TCC implements multiple measures dedicated to reducing greenhouse gas carbon emissions:
|
Climate Change Transition and Emerging Risks
Climate risks
| Item | time | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon emissions cap-and-trade/ carbon fee/ carbon tax | Increase in operational costs, decline in profitability, and creation of operational risks |
|
| Renewable energy regulations and procurement | Government penalty risk | |
| Low-carbon technology, equipment, and management cost investment | Increase in capital expenditure leading to disadvantages in market competition |
|
| Increase in raw material and energy prices | Creation of operational pressure | |
| Impact on Company Reputation | Mitigating unfavorable stakeholder views of TCC |
|
| Affecting the level of support from financial institutions in investment, financing, and insurance | Affecting investment willingness and generating operational risks | |
| Drought (Production) | Increase in operational costs and impact on operational activities | Climate disaster adaptation |
| Flood (Production) | Government penalty risk | |
| Changes in precipitation patterns and extreme changes in climate patterns (Transportation) | Increase in operational costs, decline in profitability, and creation of operational risks | |
| Drought (Production) | Increase in operational costs and impact on operational activities | Low carbon and negative carbon technology innovation |
| Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) advanced technology breakthrough | Increase in operational costs | Low carbon and negative carbon technology innovation |
Emerging risks
| Item | Time | Item |
|---|---|---|
| War and geopolitical conflicts | geopolitical issues | The South China Sea holds an important strategic position. In the event of a geopolitical conflict, it could significantly disrupt Taiwan's energy supply, thereby affecting TCC's ability to secure energy resources. In addition, the South China Sea conflict will affect the import of low-alkali sand, a key raw material for Taiwan's cement plants, impacting the stable supply of low-alkali sand. |
|
| Talent recruitment and succession | Society | An imbalance between labor supply and demand may make it challenging for companies to recruit suitable personnel to handle future unpredictability. As demand for transformation and talent in new fields rises, companies need to enhance external talent recruitment and adjust internal functions, thereby increase overall personnel costs |
|



