R&D and Certifications

The International Energy Agency (IEA) suggests reducing the clinker-to-cement ratio as one of the key measures for decarbonizing the cement industry. TCC is actively investing in and developing alternative materials, blended cement technologies, and innovative processes to significantly lower its overall carbon emissions.
The World's First Kiln-less Cement Plant
TCC's subsidiary, CIMPOR Africa's Kribi plant in Cameroon, is the world's first kiln-less cement plant.
Due to the extensive use of low-carbon calcined clay replacing traditional high-carbon emission clinker, the production process does not require high-temperature calcination in a cement kiln.
Extensive use of local raw materials reduces clinker imports by 40-50%.

New Carbon Reduction Materials
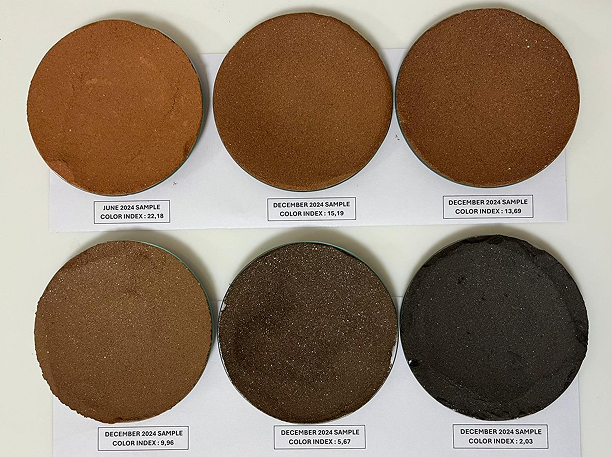

Calcined Clay, deOHclay
TCC's subsidiary, Cimpor, possesses globally leading calcined clay production technology.
Their calcined clay, deOHclay, does not contain carbonates, meaning it doesn't produce carbon dioxide during heat treatment, only releasing water vapor and trace emissions.
This results in a 90% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to traditional Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) clinker.
Cimpor is actively evaluating the calcination potential of local natural clays to explore more green material sources that can replace clinker.
Production has already started in Côte d'Ivoire and Cameroon, with future plans to expand production in Ghana.

Cocoa Pod Husks and Cashew Nut Shells
TCC's Kribi plant in Cameroon, Africa, uses local cocoa pod husks and cashew nut shells as biomass fuel, replacing coal. This reduces carbon emissions by 40% compared to traditional cement plants.

Natural Pozzolana
Cimpor's Cape Verde plant, located in the upper left sea area of Côte d'Ivoire, possesses abundant natural pozzolana resources.
Natural pozzolana has 0 kg of carbon emissions per ton. For example, in CEM II 42.5 cement, it can directly replace traditional clinker, which has 750-800 kg of carbon emissions per ton.

Waste Glass Fiber
TCC is collaborating with printed circuit board manufacturers to research and develop the use of waste glass fiber generated from PCB manufacturing processes as an alternative raw material. The goal is to obtain individual case reuse permits by the end of 2025.
Glass Micro-powder
Given the risk of raw material shortages in the cement industry, the development of new materials is becoming increasingly important.
Glass is a silicoaluminate material, and through the recycling and grinding of waste glass, it can be used as a pozzolanic material.
A patent for this was successfully obtained in 2025.
New Carbon Reduction Technologies

Development of New Hydraulic Material, X-Clinker
Significant reduction of CO2 emissions down to 340 kg CO2/ ton
Several studies of possible applications and durability in concrete
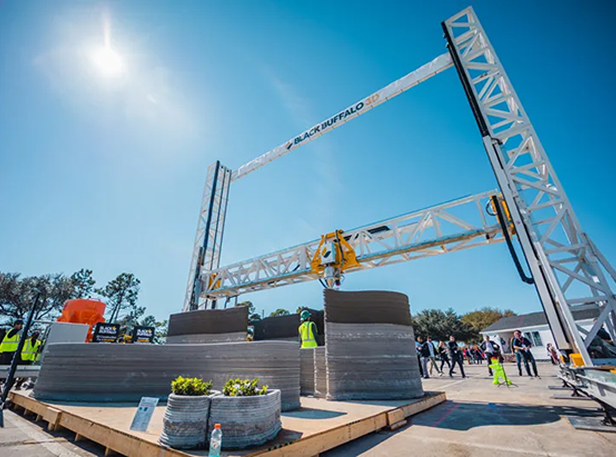

Low-Carbon 3D Printing Technology
Partnering with the world's only fully programmable construction 3D printing technology to jointly advance innovative applications in architectural printing.
Researching and manufacturing CIMPOR brand low-carbon 3D construction printing materials, using calcined clay, ground granulated blast-furnace slag, fly ash, and white and gray cement as their base.
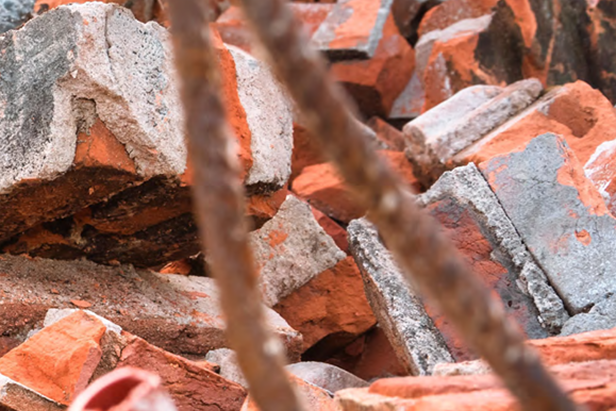

Utilizing Demolition Wastes to Produce Recycled Concrete
Targets to 100% remanufacture demolition wastes into new construction materials
Actively promoting the 'pre-carbonation treatment' technology to transform concrete by-products into a significant carbon sink
TCC has invested in low-carbon 3D printing technology and material development, researching concrete materials applicable to 3D printing, which marks a major innovation in domestic research on cement-based materials for 3D printing. TCC will continue to collaborate with domestic and international industry-academia partners to invest in low-carbon 3D printing technology, driving the development of low-carbon building technology.
Cost Effective | Stronger Strength | Adjustable color | Large-scale printing |
3D printing experimental stage

Material ratio
Fluidity
Setting time
Material strength

Small-scale testing
Extrudability
Buildability

Small-scale printing
Buildability
0.5*0.5*0.5 m

Large-scale testing
Pumpability
Buildability
Large-scale printing
Buildability
Implementation stage
3*3*3 m
Global Innovation Hubs
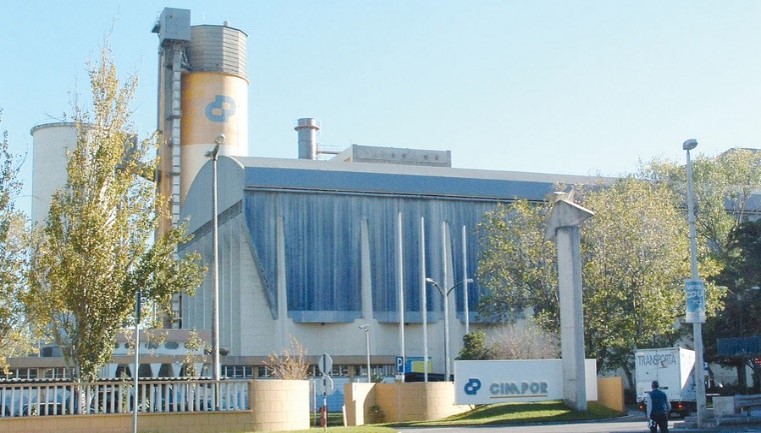

CIMPOR Central Laboratory
Dedicated to innovative research in low-carbon building materials, actively developing new products and solutions with environmental benefits.
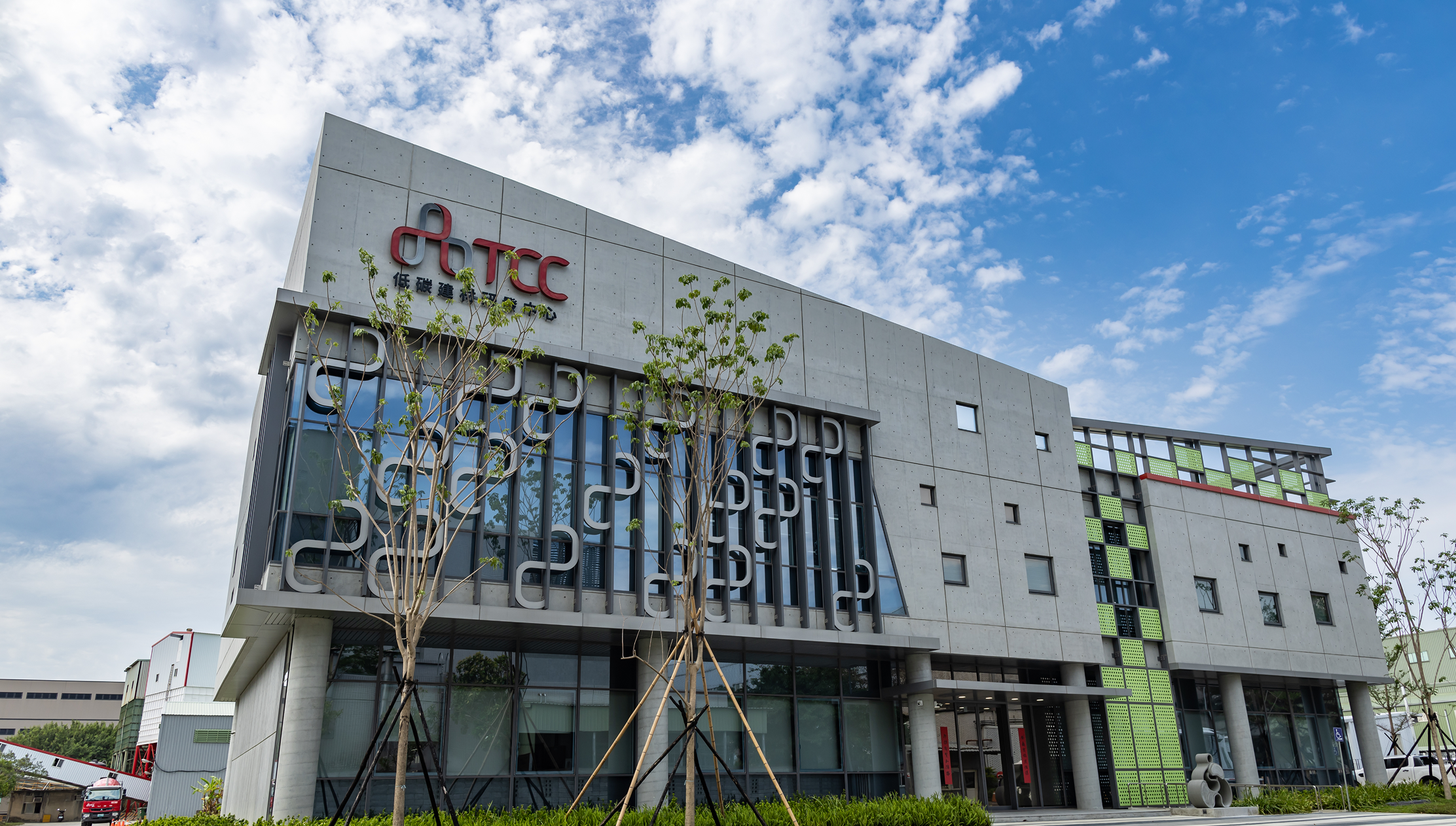

Low-carbon R&D Center
An internationally certified TAF-level laboratory for cement and concrete, ensuring TCC's product quality and safety.
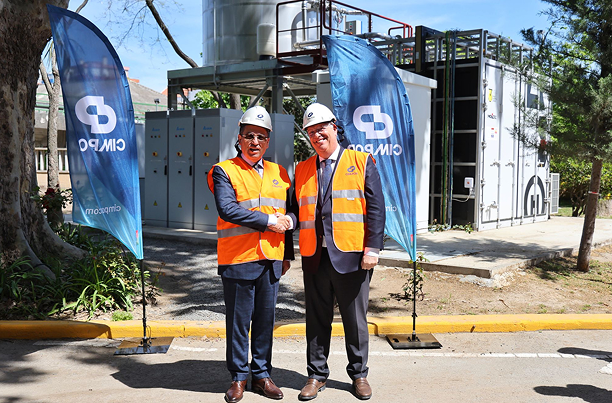

TCC Subsidiary CIMPOR to Invest €155 Million in New R&D Center
In April 2025, Portuguese Minister of Economy, Pedro Reis, visited the Alhandra production center, expressing his support for Cimpor's dedication to decarbonization technologies.
The new R&D center itself will embody sustainability principles, utilizing calcined clay cement and recycled aggregates in its construction.
The center's research focus will be on cutting-edge technologies including low-clinker cement development, carbon capture and alternative fuels, the using of recycled concrete and 3D printing technology.
Certifications
CIMPOR Central Laboratory
The Central Laboratory has gained the accreditation necessary to perform 60 tests, in a total of over 200 different tests.
Accredited with international certifications including NP EN ISO/IEC 17025 and NP EN ISO 9001.

TCC Low-carbon R&D Center
A TAF-certified laboratory for cement and concrete, meeting international standards.
The only company in Taiwan to obtain dual certification of carbon label and carbon reduction label from the Ministry of Environment.
One of the few responsible products on the market that meets international standards with certified documentation.
TCC includes carbon emission information on the invoices and delivery notes for every batch of concrete.